Attack on Armenian Church in Shushi Possible War Crime: Human Rights Watch
- (0)

Human Rights Watch (HRW) says Azerbaijani forces attacked a church in the town of Shushi during recent fighting over the breakaway Nagorno-Karabakh region, in what the group said appeared to be a deliberate targeting in violation of the laws of war.
Armenia accused Azerbaijan of shelling the Holy Savior Cathedral, a historic church perched on a strategic clifftop in Shushi, on October 8.
In a statement on December 16, HRW said the two separate attacks “suggest that the church, a civilian object with cultural significance, was an intentional target despite the absence of evidence that it was used for military purposes.”
Two separate attacks, hours apart, on the Ghazanchetsots Cathedral on October 8 in the town of Shushi suggest that the church, a civilian object with cultural significance, was an intentional target despite the absence of evidence that it was used for military purposes.
“Remnants of the weapon Human Rights Watch collected at the site corroborate the use of guided munitions. President Ilham Aliyev said that the church could have been targeted only by mistake and was “not among military targets.” The attacks took place while Armenian forces still controlled the city,” HRW said.

“The two strikes on the church, the second one while journalists and other civilians had gathered at the site, appear to be deliberate,” said Hugh Williamson, Europe and Central Asia director at Human Rights Watch. “These attacks should be impartially investigated and those responsible held to account.”
The Cathedral, constructed in the 19th century and an important building for the Armenian church, was attacked twice in the afternoon on October 8. No one was injured or killed in the first strike as the civilians in the church at the time were sheltering in its basement, but three journalists for Russian outlets were injured in the second strike. Reports of the first attack were posted on social media channels beginning around 12:30 p.m.
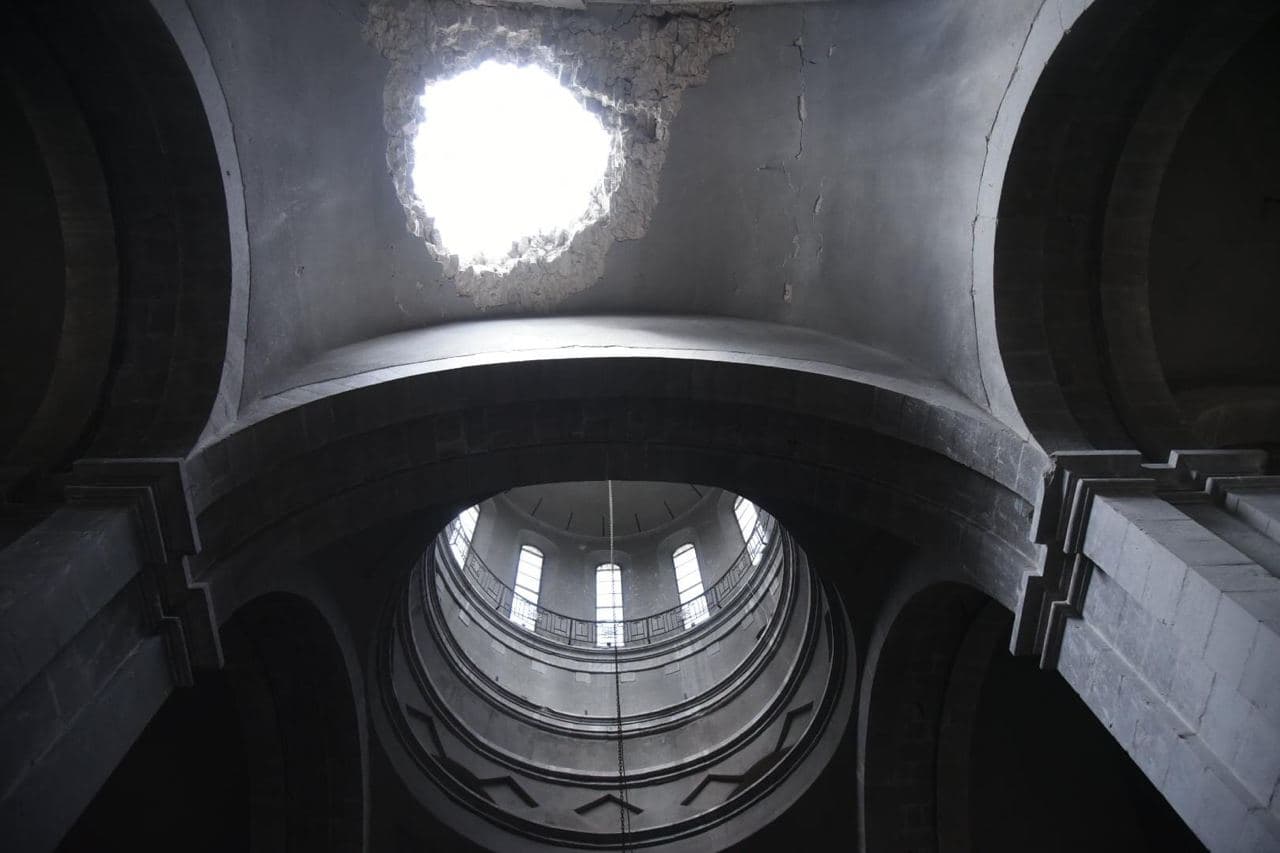
Shortly after the first attack, journalists began arriving at the church grounds. Numerous photos and videos of the damaged exterior and interior were posted online.
The damage included a hole approximately one-meter wide in the church ceiling, just south of the main dome. Debris from the blast could also be observed on the church grounds. In photos circulated at that time on social media, remnants from a weapon can be seen, consistent with a munition capable of being accurately directed at a specific target, including components that support the movement of other pieces, such as fins or wings, consistent with a device that has a terminal guidance system.
Yuri Kotenok, a journalist who arrived in the afternoon, said he didn’t see any military equipment or personnel.
Around 5 p.m., the church was attacked again. Kotenok, Levon, Arzanov, and Vahram – who asked that his real name not be used –, all journalists, were inside during the strike.
Vahram said that no one else was in the church at the time and that they were headed toward the exit when the strike hit:
- “At that moment there was a blast, a powerful one, we all were scattered… [T]here was total darkness… then the dust started to settle. I was near Yuri. We tried to take him from underneath the rubble; I could not. I got out to the street…[M]y hand was torn, and I had injuries on my back and on my head.”
Kotenok also described the moment of the attack: “I heard an awful crack and then it was hell and my friend was knocked down and flew. There was shouting and blood and he was trying to ask if I’m alive and I was trying to articulate that I was, but I was under stones and wood.”
Kotenok said he was carried out of the church and transported to the hospital in Stepanakert for surgery, then airlifted to Yerevan.
The Azerbaijani government has denied intentionally striking the church, instead asserting without evidence that the church was attacked by Armenian forces as a “provocation” or that it may have been mistakenly struck by Azerbaijani artillery.
However, the Human Rights Watch says, multiple factors indicate that both attacks were directed at the church. The remnants found indicate that the weapons used were capable of being directed at a specific target. The two strikes struck the same part of the church roof, with no more than two meters difference between the point of impact. This substantially reduces the possibility that less precise weapons were used, given their inability to achieve such a high degree of accuracy over two strikes. Additionally, Human Rights Watch is not aware of any additional reports of strikes in Shushi around the church at the time of these attacks, suggesting that each attack was a single strike.
International humanitarian law, also known as the laws of war, requires warring parties to distinguish between civilian objects and military objectives at all times. Attacks directed at civilian objects that are not used to commit hostile acts or are otherwise not military objectives are prohibited and may constitute a war crime. Warring parties are also required to respect cultural property and special care must be taken to avoid damage to buildings dedicated to religion and historic monuments. They must not be attacked unless imperatively required by military necessity.
“Serious violations of the laws of war committed with criminal intent – deliberately or recklessly – are war crimes. Governments have a duty to investigate allegations of war crimes by members of their armed forces or forces on their territory and to fairly prosecute those found responsible,” HRW says.
“It has been over a month since Azerbaijan has retaken control of Shushi and the government needs to waste no time in investigating the attacks and holding those responsible to account,” Williamson said. “Attacks such as these serve no military purpose and all parties should ensure these kinds of attacks are punished and otherwise prevented.”